Disease library
1 January 2000 | 193781 views | Health and Biosecurity
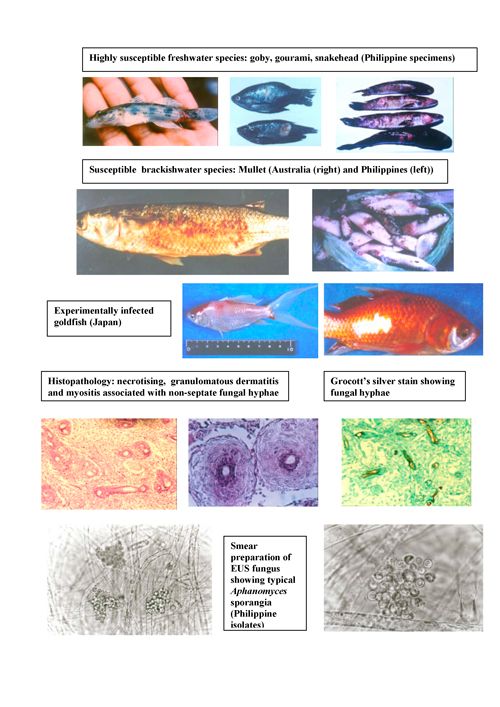
A collection of technical publications relating to aquatic animal disease prevention, diagnosis and treatment.
Creative Commons Attribution.
1 January 2000 | 193781 views | Health and Biosecurity

A collection of technical publications relating to aquatic animal disease prevention, diagnosis and treatment.
Creative Commons Attribution.