Viral covert mortality disease (VCMD): Disease card
25 May 2020 | 4757 Downloads | .pdf | 3.99 MB | Crabs and lobsters, Freshwater finfish, Freshwater prawns, Health and Biosecurity, Shrimp
This disease advisory describes the history, known host range, clinical signs and PCR detection methods for viral covert mortality disease (VCMD). Crustaceans currently known to be susceptible to VCMD include Penaeus vannamei, P. chinensis, P. japonicus, P. monodon, Macrobrachium rosenbergii, Procambarus clarkii, Exopalaemon carinicauda, Ocypode cordimanus, Diogenes edwardsii, Corophium sinense, Parathemisto gaudichaud and Tubuca arcuate. Fish species including Mugilogobius abei, Carassius auratus, and Paralichthys olivaceus may also be susceptible to the virus.
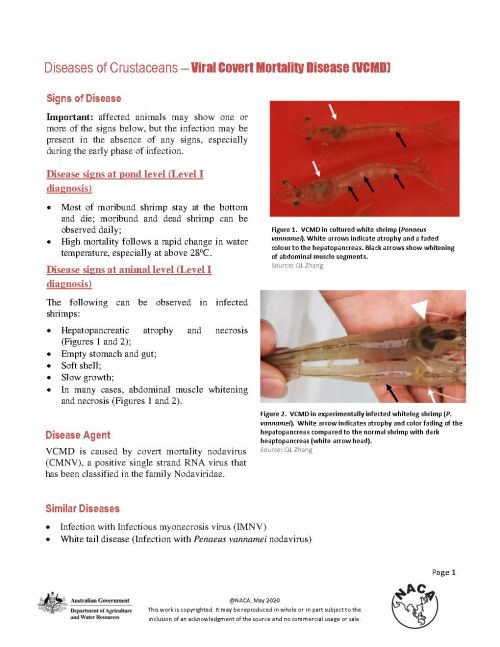
At the pond level, most moribund shrimp stay at the bottom and die and dead shrimp can be observed daily; high mortality follows a rapid change in water temperature, especially at above 28°C. At the animal level, clinical signs of infected shrimp include hepatopancreatic atrophy and necrosis; empty stomach and gut; soft shell; slow growth; and in many cases abdominal muscle whitening and necrosis.
Importantly, affected animals may show one or more of these signs but the infection may be present in the absence of any signs, especially during the early phase of infection.
Creative Commons Attribution.