In this issue:
NACA conducts workshops on white spot disease and shrimp health management in I.R. Iran. Don’t forget to register for the 11th Asian Fisheries and Aquaculture Forum! NACA pays tribute to Professor H.P.C. Shetty – Patron of the Pillay Aquaculture Foundation. EHP: Shrimp industry survey. 3rd International Conference on Fisheries and Aquaculture, 24-25 August, Negombo, Sri Lanka. Special Session on the Status of Aquatic Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture. Second International Technical Workshop on Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease (AHPND). Guidebook on Farmer-to-Farmer Extension Approach for Small-Scale Freshwater Aquaculture. Sustainable intensification of aquaculture in the Asia-Pacific region.
Professor H. P. C. Shetty (17 May 1930 - 11 November 2015) was the first Director of Instruction of the College of Fisheries Mangalore, established in 1969, the first such College in India, thereby laying the foundation for fisheries education. He was responsible for setting the syllabus and developing the campus of the College in Mangalore. He was involved in replicating the Mangalore Fisheries College model elsewhere in India and even abroad.
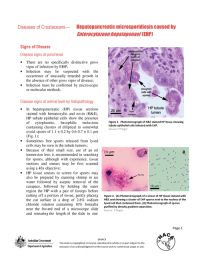
This disease card describes the diagnosis and range of a microsporidian shrimp pathogen, Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei (EHP), first discovered in Penaeus monodon in Thailand in 2004. It infects only the tubule epithelial cells of the hepatopancreatic tissue of shrimp. EHP was later found to also infect P. vannamei cultivated in Thailand and is suspected to have been reported from P. japonicus in Australia in 2001. EHP has been reported from Vietnam and is associated with white faeces syndrome.
In this issue:
Aquaculture feed supply chain attracting scrutiny. Pond beauty contest, Ram Kumar and social development. Culture modes of giant freshwater prawn in Yangtze River Delta for early harvest. Fish marketing in Kashmir, India - a case study of Srinagar. Community-based integrated fish-duck farming: A boon for rural development in agro-climatic conditions of Assam, India. Gastropod and bivalve fishery of Kakinada Bay, Andhra Pradesh, India: Management and conservation issues.