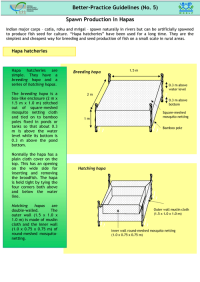
This is the annual report (2003-2004) of the Reef Fish Aquaculture R&D Project, based at the Northern Fisheries Centre, Cairns. The project provides a core platform for a suite of R&D projects addressing the feasibility of aquaculture technologies for high-value marine finfish species. This report outlines progress on the three core components of the programme, namely broodstock management and spawning, live prey production, and larval rearing and grow-out.
In this issue: Policy development as a theme and policy briefs as a genre. Decriminalising Cambodian family-scale fishers through a livelihoods approach to law reform. Longer pond leases in Orissa. One-stop Aqua Shop - a "one-window delivery" service center for aqua-farmers and fishers. Fisheries and aquaculture policy formulation process in Pakistan. Improving the international marine ornamental fish trade to sustain and improve the livelihoods of poor people involved in the trade. About the STREAM Journal. About STREAM.
In this issue:
Nursery rearing of silver barb Puntius goniotus. Artemia enrichment and biomasss production for larviculture. Seed production of mud crab Scylla serrata in India. Macrobrachium on the southwest coast of India. Fish wastes in urban and suburban markets of Kolkata: Problems and solutions. Groups of poor women farming carps in leased ponds, Bangladesh. Lymphocystis disease and diagnostic methods in China. Mesocosm technology advances grouper aquaculture in northern Australia.